
The goal of hair transplantation from the beginning was to fill the regions where baldness was installed in order to achieve density and the result as natural as possible.
Today, this natural result is completely possible using the current technique, the training of the surgical team, the technical improvement and the artistic capacity of the responsible surgeon.
fair: from 6 pm to 7:30 pm and Wednesday: from 11 am to 2 pm) which is one of the most traditional neighborhoods in the city.
The neighborhood has great infrastructure allowing easy access: either by car, subway or even by bus.
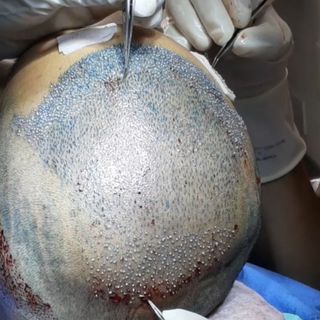
FUE technique. Removes strand from strand of neck. It does not leave a linear scar.
Clinic specializing in Hair, Beard and Eyebrow Transplants.
Reference in Hair Transplantation, specialized in FUT and FUE techniques, where the procedure is minimally invasive and leaves no visible scars.
Baldness is a problem that especially affects men, as testosterone, the male sex hormone, is the major responsible for hair loss.
Although women also produce it, there is much less in them.
Upon reaching the root of the hair, testosterone undergoes the action of an enzyme.
As a consequence of this reaction, substances appear that will reduce the speed of multiplication of the root cells or even cause their death.
The result is that the hair becomes thinner and its growth slows down.
In other words: the hair root, or hair bulb, is located in a nutrient biochemical medium so that the cells multiply and form a stem that increases in size.
These cells are renewed from the bottom up and die at the end of the wire.
The hair, after a certain time, falls out and is replaced by others, in a process of permanent renewal.
In cases of baldness, however, there is an atrophy of the hair bulbs and no new hairs grow.
Baldness is also called ANDROGENETIC ALOPECIA (AAG).
It begins in the region of the temples ("entrances"), and evolves affecting the entire scalp surface to the crown (vertex).
Classification
Male pattern baldness is classified into 7 main types, according to Hamilton-Norwood.
Subtype A is classified when baldness develops in the frontal region without forming a hair peninsula in the central region, and without affecting the vertex region (“crown”) simultaneously.
In women, the rarefaction process is diffuse, the loss occurs in the central and upper region of the scalp, without affecting the anterior line of hair implantation.
There is a transformation of a thick terminal hair into velus (down).
It is also known as Female Androgenetic Alopecia or Female Pattern of Hair Loss.
Etiology (Causes)
Female pattern baldness is as common as male pattern, but less severe, and of a totally different clinical presentation.
The onset is gradual and about 25% of women between 25 and 40 years old, and 50% of women over 40 years old, present some degree of baldness.
As in males, there is also an autosomal dominant genetic predisposition, transmitted by both parents, not only on the maternal side.
Only 20% of cases have a positive family history.
The cause is considered to be multi-factor, knowing that the conversion of testosterone (male hormone that also circulates in women, but in a smaller amount than that of men) also occurs to DHT (dihydrotestosterone), through the enzyme 5 alpha reductase .
In women, androgens (male hormones) are produced in the adrenal glands and in the ovaries.
Women have 3.
5 times less 5 alpha reductase than men, but this enzyme is also found in greater concentration in the frontal region, explaining the beginning of capillary rarefaction at this location.
Most of the time, male hormonal increases are not detected in the bloodstream.
What happens is a sensitivity of cell receptors to DHT, triggering the miniaturization process (decreasing the diameter and size of the stem of the wires and reducing their growth phase).
The triggering factors can be: hormonal disorder, including starting or stopping contraceptive use, postpartum and peri and post menopausal periods.
The main complaint of female patients is that they are able to visualize the scalp through the hair strands, when looking at each other in the mirror.
Female pattern baldness is classified into 3 main types according to Ludwig, and 8 types according to Savin.
The classification is based on the capillary rarefaction that begins at the dividing line of the hair, and that evolves laterally, affecting the entire upper surface of the scalp.